Your Score:
Your Ranking:
Daily PT Capsule Feb 18
Cabinet recommends lifting of Central rule in Arunachal
A day after the Supreme Court refused to stop the dissident leaders and the Governor in Arunachal Pradesh from forming a new government, the Union Cabinet on Wednesday 17 Feb sought the revocation of President’s rule in the State imposed on January 26.
Analysis
What is the issue all about? – Nabam Tuki became the Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh in 2011. In Dec 2014 Health and Family Welfare Minister Kalikho Pul is dropped from the government is dropped and is later expelled from the party. Mr. Pul then joins hands with 11 BJP MLAs with the backing of 19 rebel Congress MLAs. They then issue a resolution to remove the speaker. The Governor J P Rajkhowa orders to prepone the session to discuss removal of speaker. The centre then implements President’s rule in Arunachal Pradesh.
As per the Congress leaders at the centre the dissident MLAs don’t have the majority to form a government in Arunachal Pradesh.
The role of Governor? – During the whole issue the role of the Governor as a neutral party has come into question. Preponing the assembly session and removing the speaker are being questioned by the state government. Governor J.P. Rajkhowa had summoned the sixth session of the state legislative assembly for three days from December 16 in place of January 14 to 18 as scheduled earlier.
The governor’s office said that the change in dates were done in exercise of powers conferred on him under clause (1) of Article 174 of the Constitution. Â But the state government contests that the Governor cannot act without the advice of the council of ministers.
The cabinet also resolved to take legal opinion on four issues:
(i) Whether there was any provision in the Constitution which empowers a governor to pre-pone a legislative assembly‘s session?
(ii) Whether a governor is empowered under Article 174(1) of the Constitution to pre-pone an Assembly session without consulting the chief minister and council of ministers?
(iii) Whether the governor’s order of December 9 was contrary to the mandate of Rule 3 Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business?
(iv) Whether a governor can issue a message under article 175(2) of the Constitution of India fixing ‘Resolution for removal of Speaker’ as first item of business, bypassing the Business Advisory Committee of the state legislature?
Source: TheHindu, TheIndianExpress
Hybrid Maize in Punjab
To give an impetus to crop diversification, the government in Punjab, plans to replace the paddy (rice) with hybrid maize in two lakh hectares this kharif season (2016-17).
The government will go in for hybrid maize, considered the best alternative to paddy, in 14 districts. During 1976-77, maize was grown on 5.8 lakh hectares, and the area has now come down to 1.3 lakh hectares as per agricultural department.
The hybrid varieties of maize that yield 6-7 tonnes a hectare are now available, the area can be increased to 8 lakh hectares to meet the requirements of cattle feed, poultry and starch production.
The government has established a maize board to help farmers in production and marketing. The government has installed dryers in many markets at a cost of Rs. 52.85 crore because maize  has a higher moisture content of 25-30 per cent at the time of harvest. For storage, the moisture content should not be more than 14 per cent.
Analysis
Reducing area under paddy – Punjab faces serious water shortages and a groundwater table that is falling dramatically. Farmers have been tapping into groundwater supplies via tubewells. There are 1.3 million tubewells in the state, and officials say almost all farms have at least one.
Rice is the crop of choice  in many areas in India – but rice is the cause of the problem.  Farming rice paddy fields requires a lot of water – more than three times the amount of water that Punjab usually gets in rainfall each year. There is a critical need to come up with better rice plantation techniques which require less water. The other option is to diversify crops from paddy. Maize can be a good choice in terms of returns for the farmer and sustainability.
Source: TheHindu, PRI.org
Proposal for gravitational wave detector approved
Days after an international team of scientists, including several from India, formally announced that it had detected gravitational waves from deep space, the Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, said it had, “in principle,†approved a proposal to have a gravitational wave detector in India.
Current estimates suggest the project would cost at least Rs. 1,200 crore. It will take minimum eight years to get the project up and running.
Analysis
What is the gravitational wave detector? – Â A gravitational-wave observatory (or gravitational- wave detector) is any device designed to measure gravitational waves, tiny distortions of spacetime that were first predicted by Einstein in 1916.The project will be led by the Indian Initiative in Gravitational-wave Observations (IndIGO), which has been a member of the international LIGO collaboration since 2011
In February 2016, the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) team announced that they had detected gravitational waves from a black hole merger.
Spin off Benefits – LIGO-India project will establish a state-of-the-art gravitational-wave observatory in collaboration with LIGO Laboratory run by Caltech and MIT. LIGO-India will bring “considerable opportunities” in cutting-edge technology for Indian industry. The project will motivate Indian students and scientists to explore newer frontiers of knowledge and will add impetus to scientific research.
Source: TheHindu, PhysicsWorld
Private sector to build fighter jets in India
Defence Minister Manohar Parrikar said that India will select one or two fighter aircraft which will be manufactured locally by a private company under Make in India initiative. This is in addition to the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA), the production of which is being scaled up.
India and France are in advanced stage of talks to conclude an inter-governmental agreement for the direct purchase of 36 Rafale fighter jets. This fighter aircraft will likely be other than the Rafale.
There are several proposals that are under consideration and “through proper process we may select them to make in India.â€
Even as the Rafale talks are on, it is not a replacement for the much smaller MiGs in service which are now being phased out.
With this, companies who lost out in the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft contest, have been pitching their aircraft in anticipation of a comeback into the race. Boeing and Lockheed Martin of the U.S. and Saab of Sweden recently gave their detailed plans.
The defence ministry is in an advanced stage of giving approval to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for setting up a second assembly line for the LCA to increase the production rate from eight to 16 aircraft per year.
The Air Force is expected to induct over 100 of the improved LCA which will feature an Advanced Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, mid-air refuelling and improved electronic warfare suite in addition to other minor improvements.
Analysis
Indigenisation of Defence – India is the largest weapons importer in the world. Although the country has now diversified its acquisition sources beyond Russia to the West and Israel, recent deals have failed to include transfer-of-technology (ToT) clauses.  If this trend continues, India’s defence technology base will continue to remain low and the country will remain dependent almost solely on imports for major defence acquisitions.
Whatever India procures now must be procured with a ToT clause being built into the contract even if it means having to pay a higher price. The aim should be to make India a design, development, manufacturing and export hub for defence equipment in two to three decades with cooperation from Private sector.
Source: IDSA, TheHindu
Take the Quiz below to know your preparation Level!
Your Score:
Your Ranking:
Daily PT Capsule Jan 17
IT Department Notice to Vodafone
The IT department has slapped a notice on Vodafone asking the company to pay Rs 14,200 crore in tax bill, which is still undergoing international arbitration proceedings, or it may face asset seizures.
According to Bloomberg News, deputy commissioner of income tax informed the company’s Vodafone International Holdings BV Dutch unit of its dues in a letter dated 4 February. Any overdue amounts, even from overseas companies, may be recovered “from any assets of the non-resident which are, or may at any time come, within India,” the agency said.
The UK-based company said that the dispute was currently the subject of international arbitration, but expressed its surprise and dissent on the development.
Analysis
Why Vodafone has been asked to pay tax? – In 2007 Vodafone International Holdings BV decided to expand its footprint in the Indian mobile phone market by buying out Hutchison Essar. But it decided to take the roundabout route; its subsidiary exchanged cash for shares with a similar holding company for Hutchison Essar, in far off Cayman Islands.
The Supreme Court ruled in 2012 that Vodafone’s actions were “within the four corners of lawâ€. It also advised Indian taxmen to “look at†the transaction instead of “looking through†it to attribute motives to the deal. What the Indian government saw however was over ₹20,000 crore in unpaid taxes, interest and penalty slipping out of its hands.
The government came up with the General Anti-Avoidance Rule (GAAR). This rule basically said that the government could dig up past deals, all the way back to 1962. There was a huge hue and cry and GAAR was postponed to 2016.
What is the status of the case? – The Indian government stated in 2014 that existing tax disputes, would be resolved through existing judicial process. The British telecom major had dragged the government to international arbitration and invoked the Netherlands-India bilateral investment protection treaty following the government’s move to tax the company. The matter is currently before an arbitration panel, to which both the government and the company have named their judges.
Source: Economic Times, TheHindu
8th Round of Delhi Dialogue
Delhi Dialogue is scheduled to begin on 17th Feb, Wednesday with focus on impact of the U.S.- led mega trading and political blocs on India-ASEAN ties.
One emerging mega bloc, the Trans Pacific Partnership (TPP), received a major boost recently with the joining of Brunei, Vietnam, Malaysia and Singapore. Diplomats are concerned that India will have to adjust to the new set of security and economic rules as increasing number of Southeast Asian countries join TPP, which began taking shape with the arrival of President Barack Obama to the White House in 2009.
Apart from economic affairs, the Dialogue is expected to feature extensive discussions on cyber security, counter-terror, and political coordination for multilateral platforms like the U.N.
Analysis
What is the Delhi  Dialogue? – The India-ASEAN Delhi Dialogue is an annual international conference of political and economic leaders, officials, academics and opinion-makers of ASEAN countries with their Indian counterparts to discuss how to intensify and broaden political, strategic, economic and civil society interaction between the two regions.
With domestic imperatives of resilience converging with regional imperatives of peace and stability, the members of ASEAN and India now look to expand areas of cooperation.
Since its first edition in 2009, Delhi Dialogue has evolved into a useful forum for brainstorming on all aspects of the ASEAN-India relationship and has contributed immensely towards strengthening of the Strategic Partnership established in 2012.
Source: TheHindu, DelhiDialogue.org
Indigenous Anti-radiation missile trial
Captive flight trials of an advanced, state-of-the-art Air-to-Surface Anti-Radiation Missile (ARM) are planned for April-May this year, and the maiden flight test by year-end by the missile technologists of the Defence Research and Development Organisation.
The range of the missile is 100 to 125 km and it will be mounted on combat aircraft Sukhoi (Su-30) and Tejas-Light Combat Aircraft.
According to DRDO sources, scientists will evaluate the performance of the seeker, navigation and control system, structural capability and aerodynamic vibrations during the captive flight trials. These will be followed by ground testing and the missile will be fired from Su-30 during the actual flight trial by year-end.
The entire missile is being developed indigenously, including the seeker. The missile will be inducted in about two years after conducting a number of developmental trials.
Analysis
What is an Anti-Radiation missile? – Â An anti-radiation missile (ARM) is a missile designed to detect and home in on an enemy radio emission source. Typically, these are designed for use against an enemy radar, although jammers and even radios used for communications can also be targeted in this manner.
Only a few countries, including the U.S. and Germany, have ARMs at present.
Source: TheHindu, Wikipedia
Saudi Arabia, Russia, agree to freeze oil output
Top global  oil producers Saudi Arabia and Russia agreed on Tuesday  16th Feb to freeze oil output in a bid to shore up prices after a 70 per cent drop due to chronic oversupply.
Saudi Oil Minister Ali al-Naimi said the move — which is conditional on other major producers joining in – was designed to stabilise the market following the dramatic price fall since mid-2014.
The announcement followed a closed-door meeting in Doha between Saudi Arabia — the de facto leader of OPEC – Venezuela, Qatar and Russia, which does not belong to the oil cartel.
Analysis
Why have the oil prices plummeted?
1) Over Supply – The International Energy Agency said that the world’s stockpile of oil sits at a record three billion barrels and it has been growing.Demand growth has risen to a five-year high of nearly 2 [million barrels a day]…but gains in demand have been outpaced by vigorous production from OPEC and resilient non-OPEC supply.
2) The Dollar – Rise in dollar has in the run up to stopping of quantitative easing and hike in interest rate has hit the oil prices.
3) Shale production – The boom in shale industry in the US have made reduced its imports as well as contributing to the global oil supply.
4) Global Slowdown – The demand for oil has slowed down owing to a gradual slowdown in global economy. Europe has been experiencing sluggish growth and China has also cut its growth forecasts shifting to sustainable growth rates.
Why top producers did not act?
1) Geo-Economies – Saudi Arabia and other OPEC producers have been refusing to reduce output in a bid to drive less-competitive players, in particular U.S. shale oil producers, out of the market. It is a fight for geo-economic oil hegemony that the middle east countries have enjoyed for a long time.
2) Geopolitics – OPEC  has also been facing internal fissures owing to Iran-Saudi Arabia tensions in the run up to the nuclear deal. Saudi Arabia has a lower cost of production  per barrel and can bear losses as  compared to the troubled economies of Iran and Russia
Source: TheHindu, MarketWatch
Take the Quiz below to know your preparation Level!
Your Score:
Your Ranking:
The importance of 10th standard in a student’s life
Those twelve years of schooling are sufficient enough to shape the next sixty years of your life, they say. Well indeed. School acts as a pillar for students to stay strong throughout their entire life. They are completely influenced by the lessons, the teachings and the knowledge garnered during the unforgettable school life.
Every chapter, subject and standard plays a vital role in building a successful individual. While every standard has its own unique importance in one’s life; ever thought why 10th standard holds an extra weight? Class 10th is undoubtedly one of the most relevant standards of formal education. It’s that time of life when one undergoes turbulent hormonal and psychological changes, thereby marking the onset of adulthood. With power comes knowledge and with time, wisdom. The level and complexity of subjects brings seriousness and a sense of responsibility among students. Students tend to become more mature and stable. The most distinguishing feature of class 10 Board exams is that they are the first nationalised external exam for school goers.
The thought of taking the board exams gives students nightmares. They are as much scared of board exams as they are kicked about their 16th birthday. However, in the end, it’s always sheer hard work that pays for life. These exams play a significant role for those who plan to move to a different school in class 11th. Class 10th results act as a deciding factor during the admission process. It also forms an important part of resume and acts as an indicator of student’s academic performance. Many prestigious colleges and universities assign separate grade points to class 10th marks and heavily rely on them while granting admission to the students.
Students study various subjects till class 10th only because they are required to choose a specialised stream thereafter. Hence, class 10 is a career shaper, a game changer. Students study all the subjects thoroughly and try to figure out their interests. Based on that and their performance in exams, they decide which stream to opt for. This is how class 10th helps students in sorting their choices and decision-making, thus enlightening the path to successful careers.
The content of all the subjects has its own significance. Students need to know a bit of every field and this knowledge makes them develop and grow infinitely; makes them sensible and responsible citizens. Thus creating a vision to achieve what seems impossible. No matter how much students dislike this standard and the board exam, when they grow up they truly realise the importance of standard 10th. Nothing can ever undermine its value in one’s life.
Demistify the approach to crack SSC and Banking Exams
With close to 1.25 lakh vacancies across Banking, SSC and Railway examinations, the sectors provide exciting opportunities to aspirants looking for government jobs.
In the era of cut throat competition, walking on the set path is not going to help you in achieving the results. You need to keep an open mind to look out for several options to opportunities that you can exploit.
Government and ministry jobs not only provides you with reputation but also gives you high salary and perks. SSC 2016 is opening a great plethora of avenues that one can explore.
Knowing the goal is critical but not good enough.The ability to put in 6- 10 hours a day for a couple of years, the ability to deal with failures along the way, the ability to know what is the smart way forward. In essence, being fully equipped to chase the goal down – That is the key! Come and join us at Career Junction 2016 on 21st Feb to explore the opportunities and the ways to get your dreams transformed into reality.
Ankit Agarwal, Product Head Banking and SSC, CL will be shedding light on educating the students on the methodology and the course of action one needs to follow to crack the exam pattern. His sessions have been proved to be very inspiring and educative for the students. Register for the session at http://www.careerlauncher.com/careerjunction/
Daily PT Capsule Feb 16
Undervalued Exchange Rate for growth
At the India MSME Summit-2016 organised by the Confederation of Indian Industry(CII)  RBI Governor Raghuraman Rajan said that Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the government don’t favour undervaluation of the exchange rate as a means to spur economic growth.  China, Japan and Korea have been examples who have promoted export driven growth through a sustained undervalued exchange rate.
Dr. Rajan said. “I personally believe that sustained undervaluation over a long period of time is not a feasible or desirable strategy. Which is why I firmly believe that the RBI’s philosophy of not focusing on the level of exchange rate and trying to manipulate it up or manipulate it down but trying instead to minimise situations of extreme volatility and intervening in situations when the exchange rate becomes extremely volatile in either direction is the right one,†he said.
The advantage to Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) should come from their capabilities, cost-effectiveness and innovative ideas rather than from undervaluation, he pointed out. MSMEs can act as a means of social empowerment where disadvantageous sections of society can be empowered with money and wealth.
Analysis
What is Exchange Rate Undervaluation – The situation of a currency whose value on the exchange market is lower than is believed to be sustainable. This may be due to a pegged or managed rate that is below the market-clearing rate, or, under a floating rate, it may be due to speculative capital outflows.
Nominal vs Real Exchange Rate – The nominal exchange rate is the rate at which currency can be exchanged. If the nominal exchange rate between the dollar and the rupee is 69, then one dollar will purchase 69 rupees. Exchange rates are always represented in terms of the amount of foreign currency that can be purchased for one unit of domestic currency.
While the nominal exchange rate tells how much foreign currency can be exchanged for a unit of domestic currency, the real exchange rate tells how much the goods and services in the domestic country can be exchanged for the goods and services in a foreign country. The real exchange rate is represented by the following equation: real exchange rate = (nominal exchange rate X domestic price) / (foreign price).
Source: TheHindu, SparkNotes
National Capital Goods Policy
The Government has unveiled the National Capital Goods Policy. Anant Geete, Minister, Heavy Industry and Public Enterprise unveiled the policy during the Make in India Week programme and said it was part of the government’s commitment to turn the country into a world class hub for capital goods.
Objectives of the policy – The objective of the policy is increasing production of capital goods from ~Rs. 230,000 Cr in 2014-15 to Rs. 750,000 Cr in 2025 and raising direct and indirect employment from the current 8.4 million to ~30 million. The policy envisages increasing exports from the current 27% to 40% of production while increasing share of domestic production in India’s demand from 60% to 80%, thus making India a net exporter of capital goods. The policy also aims to facilitate improvement in technology depth across sub-sectors, increase skill availability, ensure mandatory standards and promote growth and capacity building of MSMEs.
Aims of the policy – The aim of the policy is to create game changing strategies for the capital goods sector. Some of the key issues addressed include Availability of Finance, Raw Material, Innovation and Technology, Productivity, Quality and Environment Friendly Manufacturing Practices, Promoting Exports and Creating Domestic Demand.
Policy Recommendations – Key policy recommendations include strengthening the existing scheme of the DHI on enhancement of competitiveness of Capital Goods Sector by increasing budgetary allocation for increasing scope to further boost global competitiveness in various sub sectors of CG. The aim is to enhance the export of Indian made capital goods through  a ‘Heavy Industry Export & Market Development Assistance Scheme (HIEMDA)’. Launching a Technology Development Fund , upgrading the existing and setting up new testing & certification facilities, making standards mandatory in order to reduce sub-standard machine imports are other measures envisaged. It also aims to provide opportunity to local manufacturing units by utilising their installed capacity and launching scheme of skill development for CG sector.
Analysis
What are capital Goods? Â – Â A capital good is a durable good (one that does not quickly wear out) that is used in the production of goods or services. Capital goods are one of the three types of producer inputs, the other two being land and labor, which are also known collectively as primary factors of production.
In terms of economics one can consider capital goods to be tangible. They are used to produce other goods or services during a certain period of time. Machinery, tools, buildings, computers, or other kind of equipment that is involved in production of other things for sale represent the term of a Capital good.
Capital goods, often called complex products and systems (CoPS) play an important role in today’s economy. Aside from allowing a business to create goods or provide services for consumers, capital goods are important in other ways. In an industry where production equipment and materials are quite expensive, they can be a high barrier to entry for new companies. If a new business cannot afford to purchase the machines it needs to create a product, for example, it may not be able to compete as effectively in the market.
Therefore a robust capital goods industry is must for any form of manufacturing driven growth.
Source: PIB, Wikipedia
Djibouti Myanmar and Sri Lanka anchor Silk Road
Base in Djibouti
Djibouti’s President Ismail Omar Guelleh has been reported by Reuters saying that China will soon commence work on the naval base in Djibouti.
Djibouti would become an ideal location for securing sea lanes, in the vicinity, which radiate from this area towards Africa’s Indian Ocean coastline and the Arabian Sea.
China says it is establishing naval “support facilities†in Djibouti, which has the ambition of emerging as another Singapore, leveraging its position at the intersection of busy shipping lanes.
The Chinese facility will be established at Doraleh Multi-Purpose Port —a $590 million project that is being steered by China Merchants Holdings International in the south of the country. The Chinese Navy would use one of the berths.
Last month, Mr. Guelleh signed a deal with China to build a new free trade zone, whose first phase would open later this year. China is also providing the bulk of the $12.4 billion that Djibouti intends to invest by 2020.
Base in Myanmar
China has also quietly signed a deal to develop an Industrial Park and a deep water port in Kyaukphyu in Myanmar. The facility in the Bay of Bengal amplifies Beijing’s pitch to deepen its stakes in Myanmar in order to lower its dependence on the Straits of Malacca-a strategic commercial channel, dominated by the U.S. sixth fleet.
Xinhua has reported that a consortium led by the China International Trust and Investment Corporation (CITIC), a construction company, has won the bid towards the end of last year to develop the two projects.
Base in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka has added another dimension to China’s Maritime Silk Road (MSR). The revival of the stalled Colombo port city project under new conditions, and the establishment of an SEZ in Humbantota—both projects feeding into the gradual unfolding of the ambitious MSR.
Analysis
Horn of Africa – The Horn of Africa denotes the region containing the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Djibouti is strategically located on the junction of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea—a gateway to the Suez Canal via the Strait of Bab Al-Mandab.
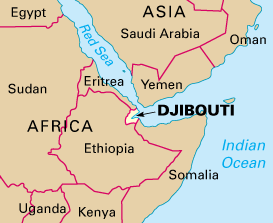
What is the Maritime Silk Road? – The 21st century Silk road which goes by the name ‘One Road One Belt’ is a Chinese initiative to reconnect with the European and African countries by reviving the ancient silk road and opening new ones through infrastructure investment. The main objective is to increase trade and economic cooperation to boost domestic growth.
The Maritime Silk Road (MSR) idea is part of this wider attempt by China to construct multiple lines of communication to its economic heartland in eastern China since the early 2000s. The underlying aim of such a geostrategy is to also develop inner Chinese provinces and shape China’s regional periphery by exercising economic, political and cultural Influence.

Source: TheHindu, IDSA
Universe’s primordial Soup
Scientists have recreated the universe’s ‘primordial soup’ in miniature format by colliding lead atoms with extremely high energy in the world’s most powerful particle accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN.
The primordial soup is a so-called quark-gluon plasma and researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute in Denmark, among others, have measured its liquid properties with great accuracy at the LHC’s top energy.
Analysis
What is Big Bang? – The Big Bang Theory is the leading explanation about how the universe began. At its simplest, it talks about the universe as we know it starting with a small singularity, then inflating over the next 13.8 billion years to the cosmos that we know today.
Because current instruments don’t allow astronomers to peer back at the universe’s birth, much of what we understand about the Big Bang Theory comes from mathematical theory and models. Astronomers can, however, see the “echo” of the expansion through a phenomenon known as the cosmic microwave background.
What is the Large Hadron Collider? – The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the most powerful particle accelerator ever built. Based at the European particle physics laboratory CERN, near Geneva in Switzerland, it is the world’s largest laboratory and is dedicated to the pursuit of fundamental science.
Source: TheHindu, Space
Take the Quiz below to know your preparation Level!
Your Score:
Your Ranking:
Daily PT Capsule Feb 15
Growing Tea Over Farmland
The Centre is at loggerheads with the West Bengal over the State government’s one-and-a-half -decade-old notification banning conversion of agricultural land into tea cultivation area.
Stating that the 2001 notification was affecting a large number of small growers – estimated to be around 20,000 – mainly in north Bengal, the Centre recently asked the West Bengal government to lift the ban. The Centre noted that the State government’s revenue authorities were not granting ‘No Objection Certificate’ (NOC) to small growers who have planted tea after the 2001 notification.
However, the State government says the ban – imposed as part of land reforms – was to prevent ‘tea gardeners’ from purchasing (forcibly and through other means such as cheating) land belonging to tribal people. The ban is also to prevent tea gardeners from illegally encroaching upon government-owned land.  Besides, the State government says the prohibition was to maintain “an appropriate environmental balance in life and livelihood†in the area. The State government had said legal action could be taken against those trying to expand tea cultivation in new areas in violation of the notification, which had followed the West Bengal Land Reforms (Amendment) Act, 2000.
Analysis
The tea gardens in the Doaars(areas of Assam and West Bengal) have been facing difficulties owing to changing climate patterns and competition by high end tea.
Recently in  January 2016 the Centre has authorised the Tea Board to take over the management control of seven gardens of the G.P. Goenka-headed Duncan Industries in north Bengal, stepping onto a populist but tricky terrain.
The Union ministry of commerce and industry invoked a rarely used section of the Tea Act of 1953 to take control of the gardens in the Dooars, saying they “are being managed in a manner highly detrimental to the tea industry and to public interest”.
According to the provisions of the Tea Act, the gardens may remain under the new management up to 12 years unless the Centre is convinced that it was no longer necessary and they can be handed back to Duncan.
The Centre can invoke the takeover clause if a tea unit made losses in three out of five immediate preceding years or habitually made defaults on the dues of workers and employees or its production yield was lower than the district average by 25 per cent or more. Industry sources said the seven gardens would qualify on all these counts.
Source: TheHindu, TheTelegraphIndia
Central nodal agency to curb human trafficking
To strengthen the fight against human trafficking, the Union government has decided to set up a central nodal agency.
Speaking on the sidelines of the fifth annual Trafficking in Persons (TIP) conclave in Siliguri, Rajnish Kwatra, Under Secretary (Prison Reforms & Anti Trafficking Cell), Ministry of Home Affairs, said the government was also mooting a law for the same.
Analysis
Operation Smile – was launched in 2015 to rescue missing children who were a victim of trafficking. 9,146 children under Operation Smile and 19,742 children under Operation Muskaan were rescued or rehabilitated in 2015 itself.
The area close to tea farms around Siliguri is prone to child trafficking due to distressed tea farms. But poverty is just one factor in such abuses. Even in highly developed economies, there is human trafficking. Material poverty does not mean poverty of values.
Source: TheHindu
Smart Card for unorganised workers
The Unorganised Workers’ Identification Number (U-WIN) scheme, first mooted in September 2014, proposed to provide a smart card to the unorganised workers for entitled to benefits under various schemes such as Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana (RSBY) and Aam Aadmi Bima Yojana (AABY) as well as the Atal Pension Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana and Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana.
It has hit a roadblock though for the second time with the Finance Ministry rejecting the latest Labour Ministry proposal to issue one card per family as an impractical idea. The Labour Ministry had originally planned to give smart card directly to all the unorganised workers, but the Finance Ministry had raised objections on the huge costs that would entail.
Keeping those budget constraints in mind, the labour ministry re-drafted the proposal to allocate one smart card to the head of each family instead of all workers in a household. But the Finance Ministry hasn’t approved of this idea either.
Analysis
Unorganized workers in India – There are around 40 crore unorganised workers in the country, which accounts for around 89 per cent of the total workforce, as per government estimates. The portable smart card would have details of bank account, mobile numbers and benefits of social security schemes that can be availed by the workers.
Clash with Aadhar – The IT ministry said that issuing smart cards to unorganised workers may lead to duplication of work as the government is already in discussions to link welfare schemes with the Aadhar card. India is already running parallel schemes like National Population Register which are adding to the exchequer. It would rather be advisable to de-duplicate all such initiatives and link it with Aadhar.
Source: TheHindu
Act against Devadasi system, SC tells States
Condemning the prevalence of the illegal practice of “dedicating†young girls as Devadasis, the Supreme Court on Friday described the practice as an “evil†done to women, who were later even subjected to sexual exploitation and pushed into prostitution.
It said that neither were the police enforcing the law nor were the State governments are properly utilising funds allocated for the rehabilitation of girls who were pushed into the Devadasi system. Additional Solicitor General claimed that State-level legislation such as the Karnataka Devadasis Prohibition of Dedication Act, 1982, and Maharashtra Devadasis Abolition Act, 2006, had completely abolished such practices. The practice of Devadasis system violates Sections 370 and 370 A of the IPC as amended through the Criminal Law Amendment Act, 2013.
Analysis
What is the Devadasi System? – In South India, a devadasi is a girl “dedicated” to worship and service of a deity or a temple for the rest of her life. The dedication takes place in a Pottukattu ceremony which is similar in some ways to marriage. Originally, in addition to taking care of the temple and performing rituals, these women learned and practiced Sadir (Bharatanatya), Odissi and other classical Indian artistic traditions and enjoyed a high social status as dance and music were essential part of temple worship.
During British rule in the Indian subcontinent, kings who were the patrons of temples and temple arts became powerless. As a result, devadasis were left without their traditional means of support and patronage. During colonial times, reformists worked towards outlawing the devadasi tradition on grounds that it supported prostitution.
The devadasi system was outlawed in all of India in 1988, yet some devadasis still practice illegally.
Source: TheHindu, Wikipedia
Take the Quiz below to know your preparation Level!
Your Score:
Your Ranking:
























































