The Supreme Court and the High Court other than having appellate jurisdiction over civil and criminal cases have another peculiar jurisdiction of issuing the writ. These writs are primarily issued, to enforce their constitutional rights. The Supreme Court however has narrower jurisdiction compared to the High Court when it comes to the issuance of the writ. High Court has the power to issue writ even in case of breach of any legal right, whereas the Supreme Court can issue writ only in case of breach of fundamental rights.
There are five types of writs:
- Habeas Corpus: means to bring the body
This writ is invoked to secure rights of liberty as envisaged under the Constitution of India.
This is the only writ that can be issued against the state as well as a private person. Such a writ may also be issued in cases:
- When the person is detained and not produced before a magistrate within 24 hours
- When the detention is done to cause harm or damage with mala fide intent.
- Certiorari: means to quash.
The writ of certiorari can be issued by the Supreme Court and the High Court for quashing the order passed by an inferior court, tribunal, or quasi-judicial authority.
-
- Such a court, tribunal, or quasi-judicial authority has passed an order without having jurisdiction or in excess of jurisdiction entrusted under law.
- When the order has been passed in violation of the principles of natural justice.

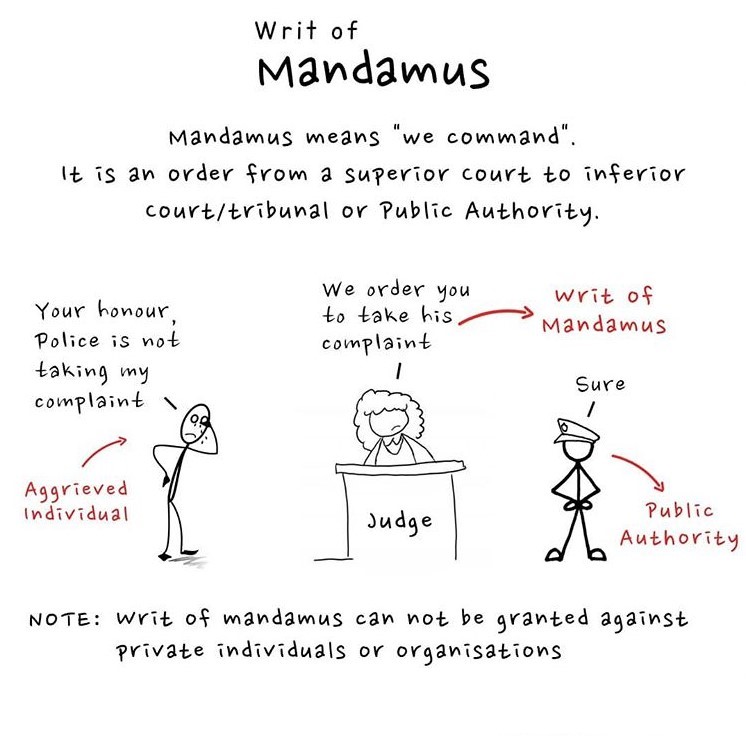
- Mandamus: means to command.
The writ of mandamus issued for commanding the lower court tribunal or quasi-judicial authority to perform their duties which they have refused to perform. Generally, the writ of mandamus is issued if the following condition is fulfilled
-
- There subsisted a legal right
- There is an infringement of the legal right of the petitioner
- There is infringement as the right is due to nonperformance of duty by the public authority
- The petitioner has demanded the performance of legal duty which has been refused.
 4. Prohibition means to prohibit any proceeding
4. Prohibition means to prohibit any proceeding
This writ is generally issued when higher court to an inferior court or quasi-judicial body prohibiting them to continue any proceeding in the lower court. The writ is generally issued when the subordinate court or tribunal hears the matter beyond their jurisdiction or matter on which they have no jurisdiction. However, apart from jurisdictional error, this writ may also be filed when an order is in violation of the principle of natural justice or the proceeding is ultra vires under the statutes.
 5. Quo Warranto means by what authority.
5. Quo Warranto means by what authority.
This writ of quo-warranto to be issued where the higher court may ask the holder of the office that by what authority he is holding the office it relates to public office. Writ of quo warranto is used to oust a person from usurping a public office






















































